PoE Basics
Welcome to this short series on PoE. In this first post, we’ll be discussing PoE Basics.
What is PoE?
PoE or Power over Ethernet is simply a technology that allows power and data to be transmitted over your ethernet cable, where traditionally only data is transmitted.
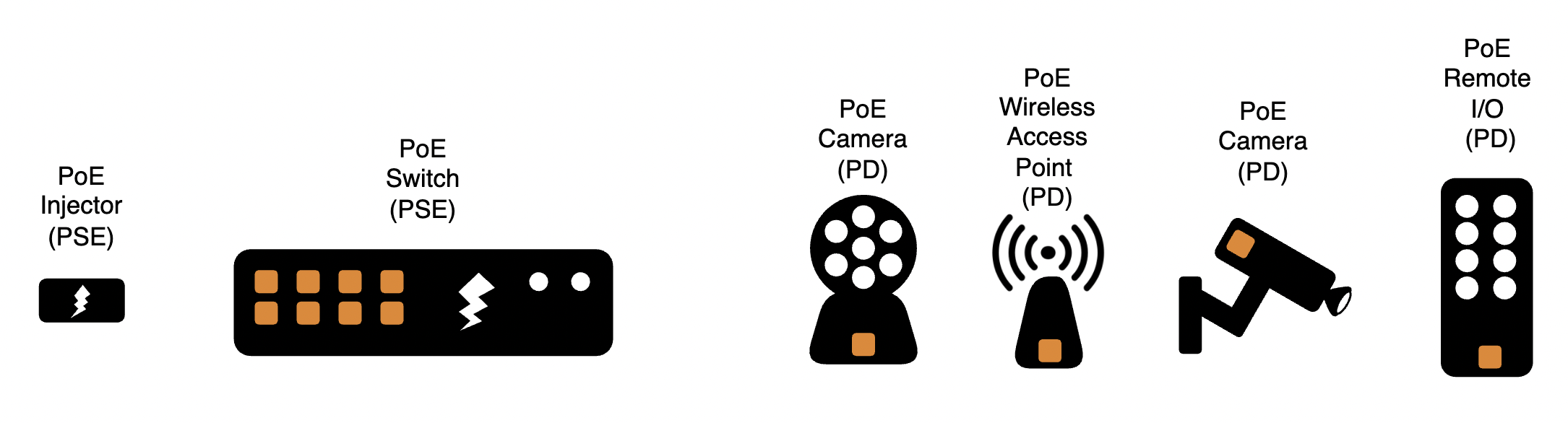
There are three components in every PoE system:
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE)
Ethernet cable
Powered Device (PD)
There are two types of PSE: Switch (Endspan) and Injector (Midspan), and there are numerous PD types from cameras to wireless access points, remote I/O, sensors, etc.
Why PoE?
PoE is a great feature to simplify installation for devices that support it. PoE allows Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) to provide power to a Powered Device (PD) across the same ethernet cable data goes across, eliminating the need for a separate power supply and running extra wiring to a field device such as an IP camera, wireless access point, or even remote I/O.
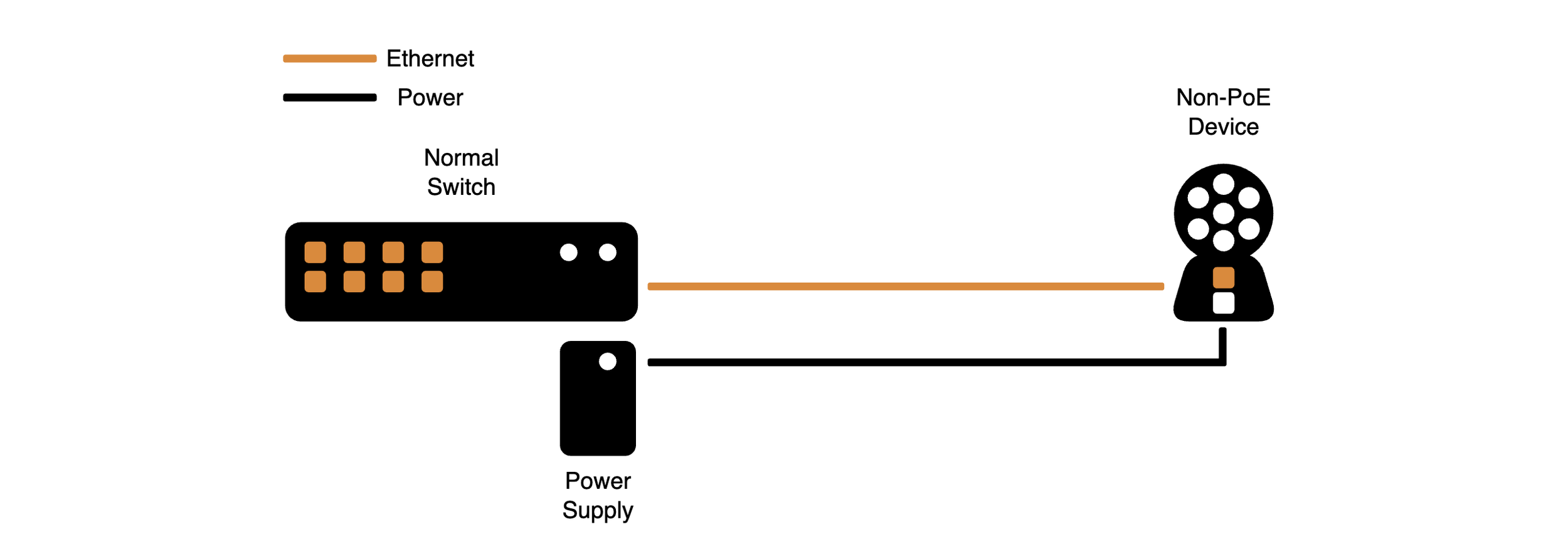
Traditional ethernet device requires separate power cable and ethernet cable
With a PoE Injector, field wiring can be reduced, but a separate power supply is still required
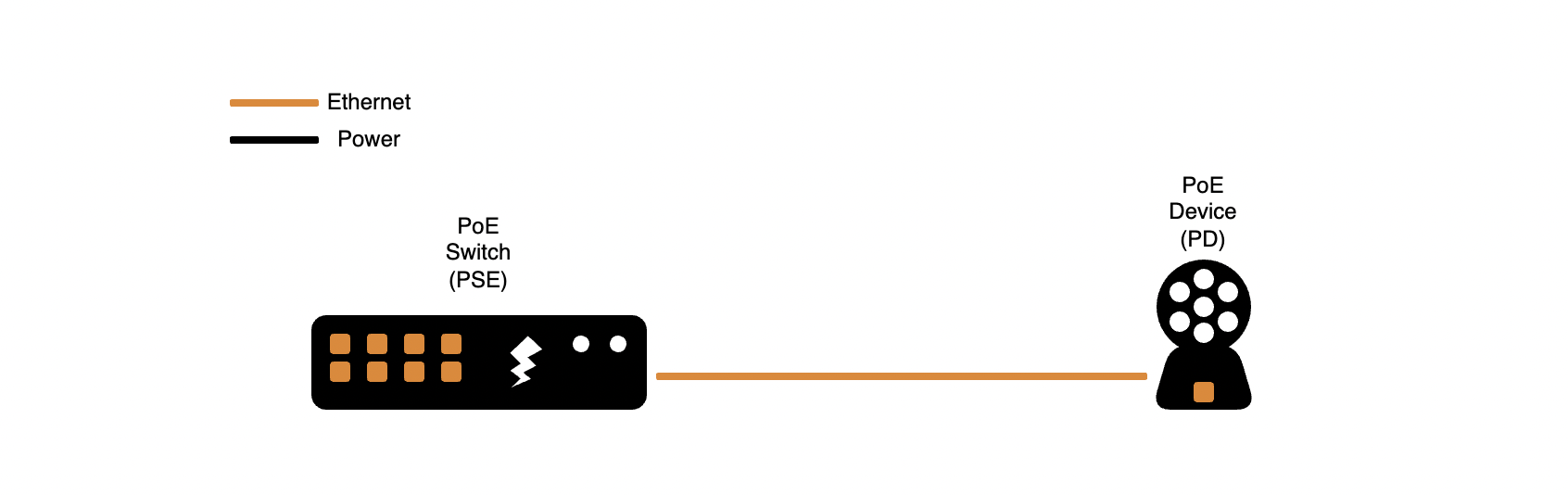
A PoE switch with a PoE PD is the simplest system, allowing for minimal equipment and reduced field wiring
PoE Benefits
PoE can save a lot of time and money during design and installation. Since there is no need for a separate power cable, there is less engineering time for power circuits, less or lower conduit costs to run for wiring, and, of course, less wiring to run.
The savings don’t stop there. Because the system is less complex, there is less that can go wrong once the system is installed.
And lastly, PoE is an enabler. You can easily add more devices to measure, record, control, connect, and analyze. With the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industrial IoT (IIoT), customers want to measure everything, and PoE is one of the technologies that facilitates that objective.
PoE Applications
PoE started primarily with IP phones on the IT side of the house, but now there are many more devices that support PoE including in OT. Some of these include:
IP Cameras
Wireless Access Points (WAP)
Network switches
Routers
Lights
Sensors
Meters
Remote I/O
HMI Displays
Wrap up
So far we’ve talked about what PoE is, some of the benefits, and common applications.
“It sounds too good to be true! What’s the catch?”
In many cases, it really is that simple - just plug and play. However, as many of you have likely encountered every now and then with a blind plug-and-play approach, you may very well have just fried your very expensive (and long lead time) IP camera/sensor/etc. 🤭
In the next blog post, we’ll discuss some of the various PoE pitfalls and how to avoid them.